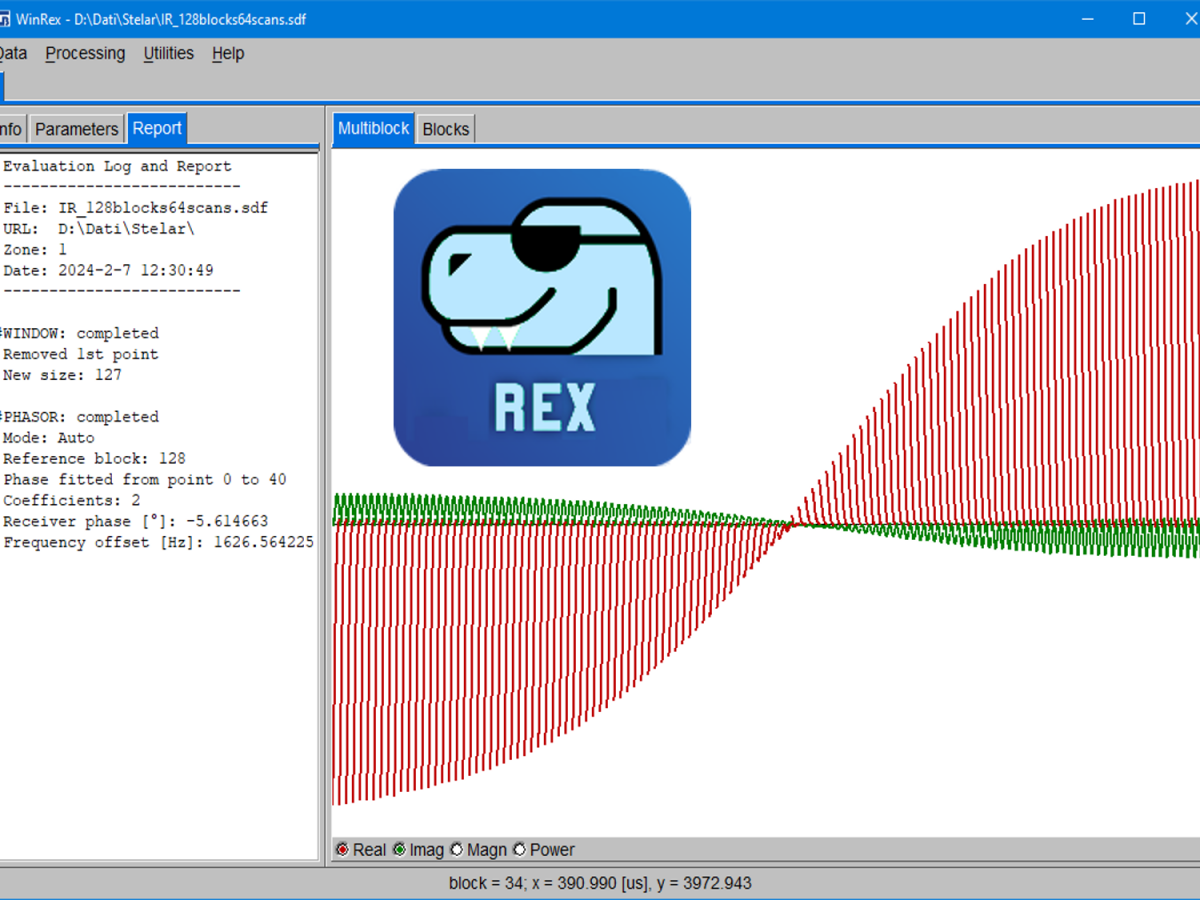
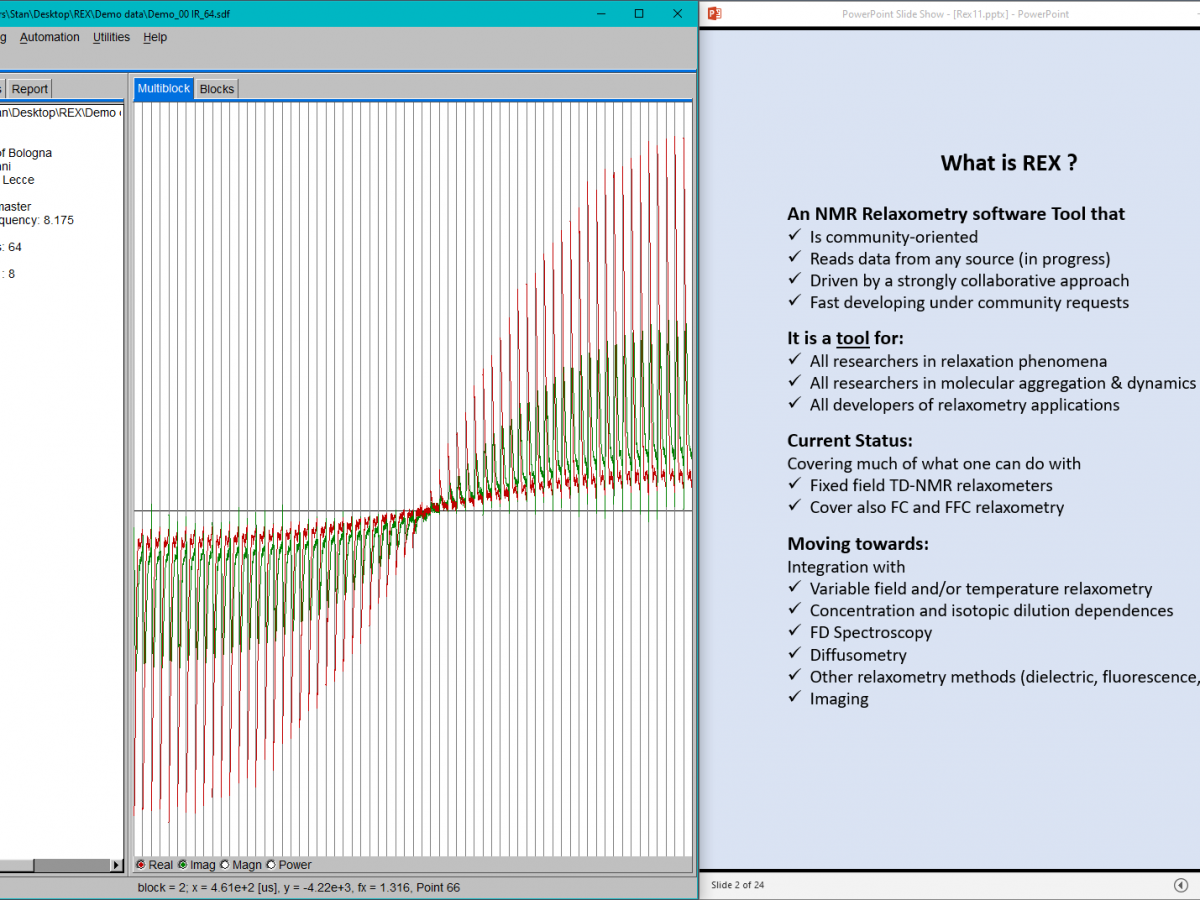
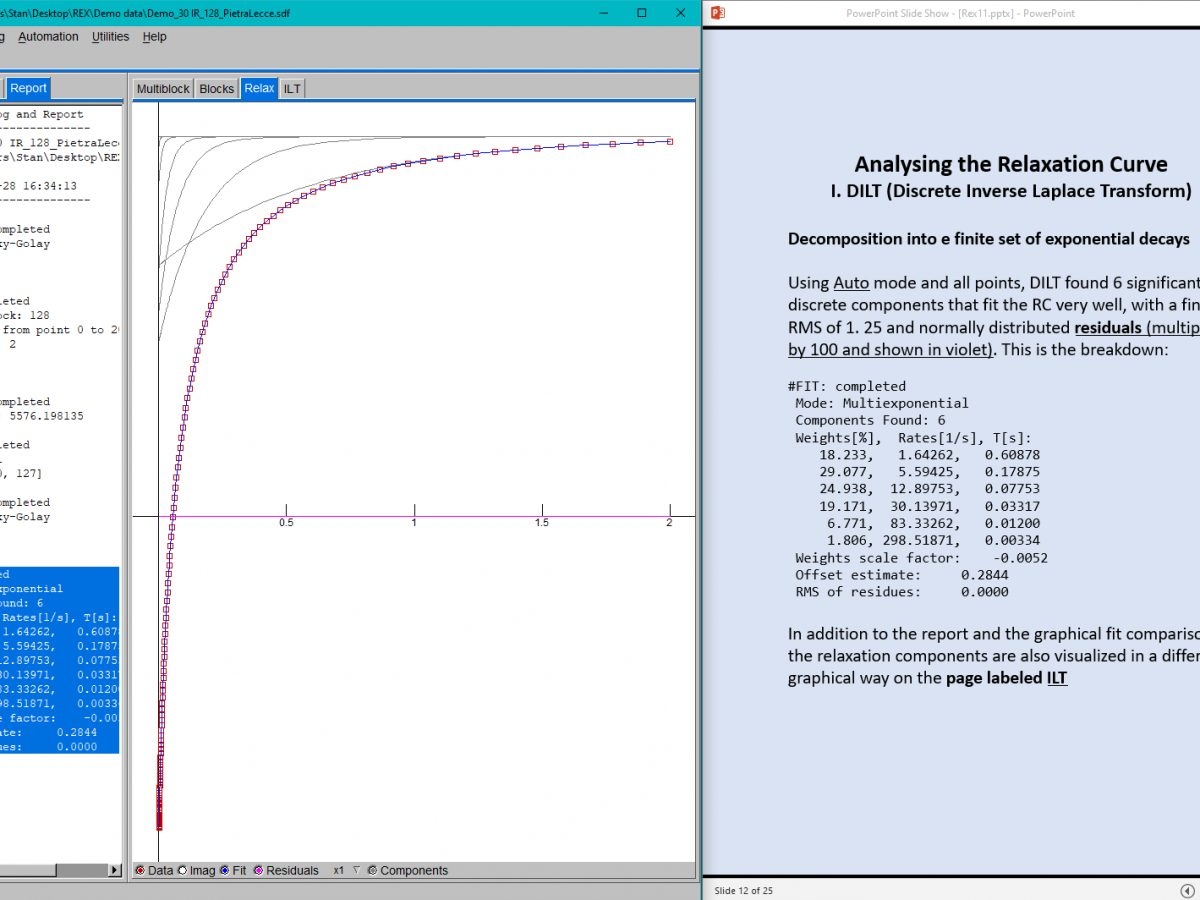
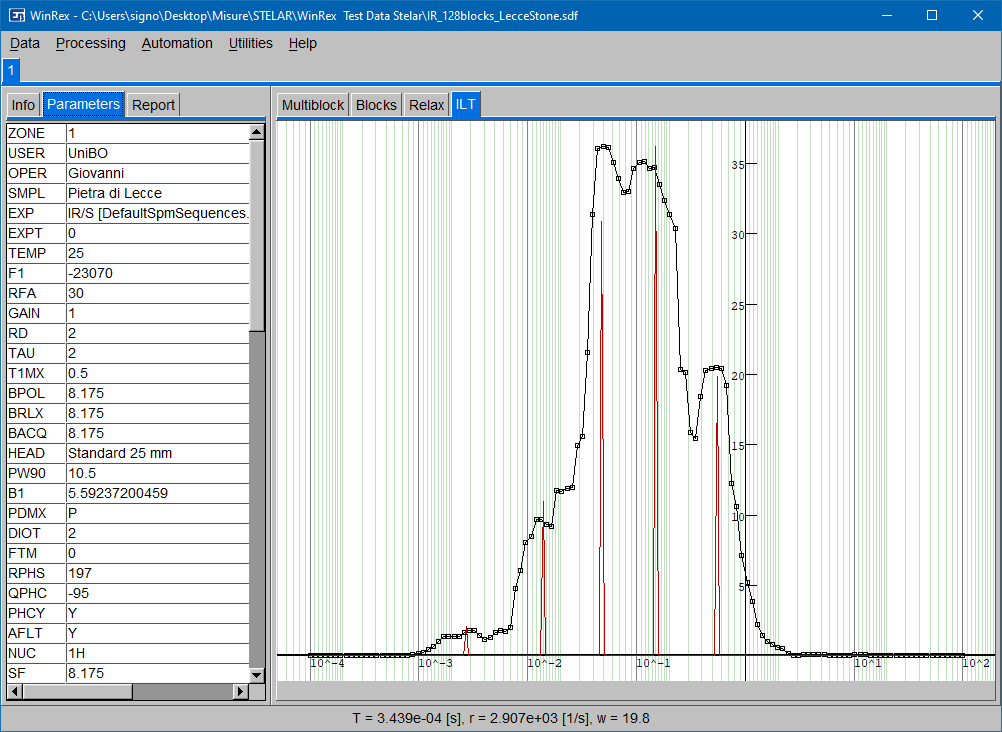
REX is a community-oriented software tool for NMR Relaxometry.
This means, above all, that it is designed to read raw data from any source. However, given the profusion of currently used data formats, not all NMR vendors are yet supported. If your data files are not simple n-column text files, Stelar files (SDF), Bruker folders (TopSpin), or Oxford Instruments files (RiDat), or if you are not sure, simply write us, send us a sample of your data file(s) and we will be glad to make sure that REX can read it. This service is free and we will do it before your demo period has started.
It also means that we wish to operate in a strongly collaborative way. For the full duration of their software license, our Users are entitled to full support, including any code modifications/additions implemented on the basis of requests that reach us from the entire NMR community (should your request embody an original idea, we will respect it and always properly cite it).
REX is a handy and pretty universal tool for:
- NMR experts who research relaxation phenomena as such
- experts who research molecular dynamics and aggregation
- developers of specific NMR relaxometry applications for end-Users non-privy to NMR
Current REX state-of-the-art:
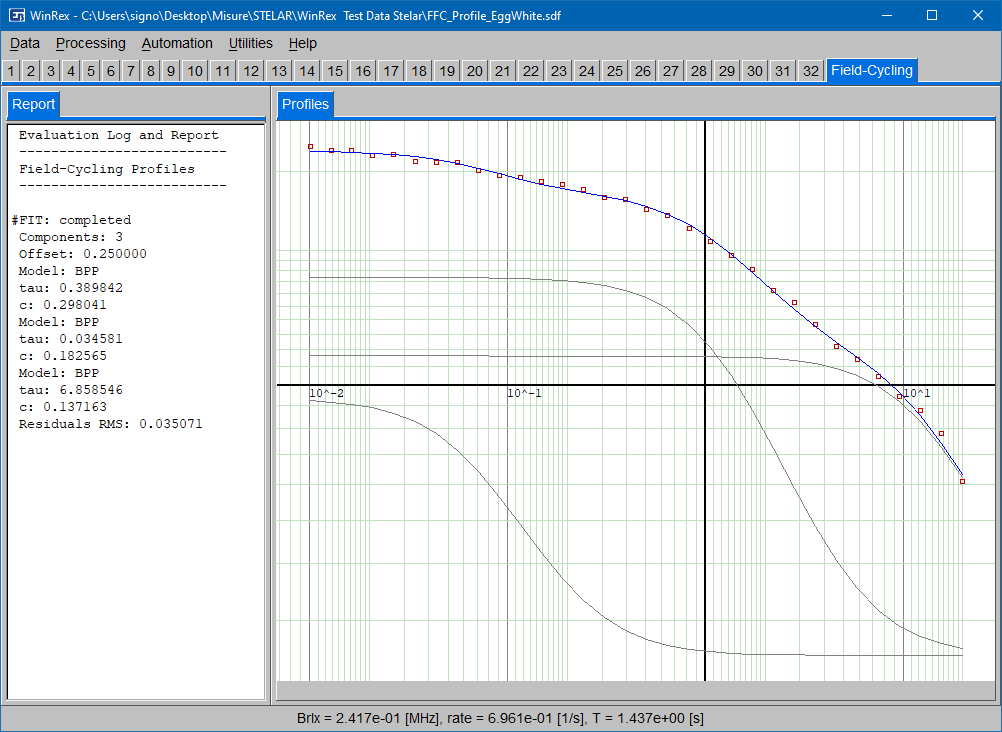
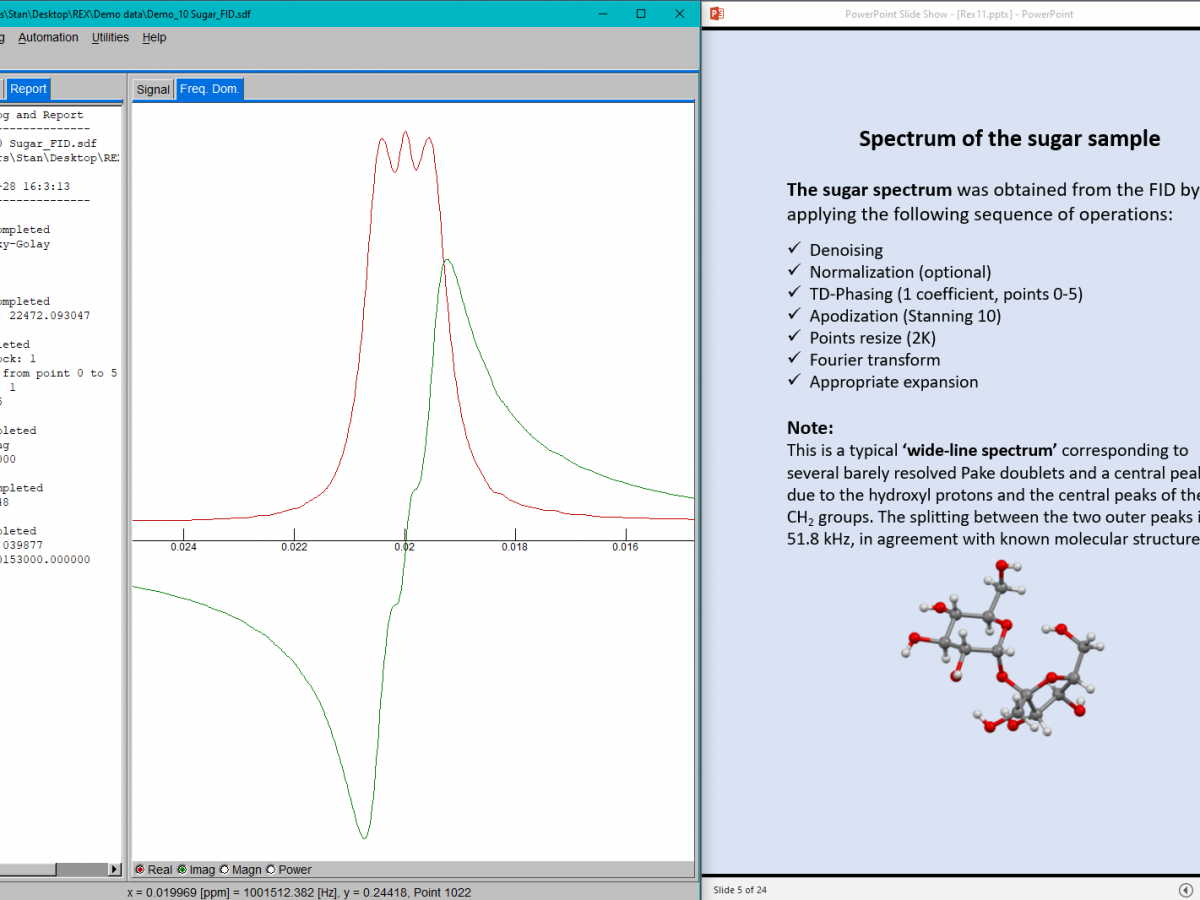
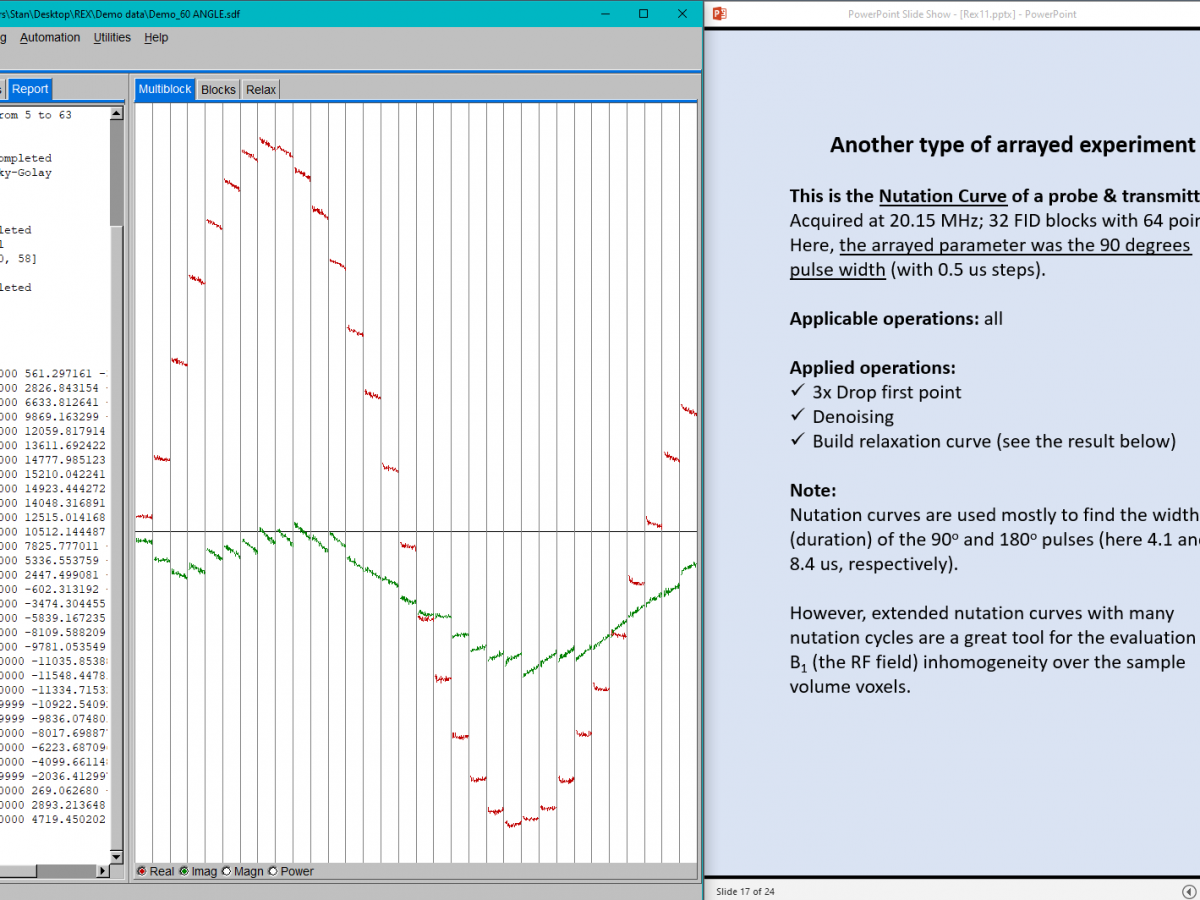
WinREX 1.0 covers almost everything that one can do with fixed field TD-NMR relaxometers, as well as with variable-field and fast-field-cycling (FFC) instruments.
For more details, please download and consult the document “The territory of Rex”.
Future oriented:
We will steer REX to provide support also for:
- Variable temperature relaxometry,
- Concentration and/or isotopic dilution dependences
- Spectroscopic variaties of relaxometry
- Diffusiometry combined with relaxometry
- Rheological and kinetic effects in relaxometry
- Other relaxometric methods (dielectric, fluorescence, …)
- Relaxometry applications in MRI